
SCIENCE

Personalized Immuno-Corrective Therapy for A Genetically Defined Population
The soluble Interleukin 7 Receptor (sIL7R) is a key driver of the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune diseases.
sIL7R is elevated by a SNP associated with higher risk of disease severity and poor response to existing standards of care.

The ABS sIL7R monoclonal antibody development program is genetically defined within a validated pathway representing a significant unmet need:
Genetically-defined: genetic variant (SNP) enhances disease activity by increasing sIL7R expression.
-
Gregory et al., 2007, Nature Genetics 39, 1083-1091.
-
Galarza-Munoz et al., 2017, Cell 169, 72-84.
Validated Pathway: sIL7R enhances T cell activity and autoimmunity in animal models and patient bio samples.
Significant Unmet Need: sIL7R is associated with risk of increased autoreactivity, poor response to therapy and disease severity across multiple diseases.
ABS Three Lead Indications are Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus / Lupus Nephritis and T1D:
Each has a ~50% Non-Response to SOC Likely Associated with Genetically Elevated sIL7R
- | RA | Lupus/ Lupus Nephritis | T1D |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard(s) of Care |
|
Approved in combination with SOC |
Slows progression from Stage 2 to Stage 3 T1D |
Non-Response Metric and Rate |
|
|
|
Evidence Suggesting the Role of Elevated sIL7R in Non-Response | High sIL7R associated with 3-fold difference in response to infliximab | High sIL7R associated with high proteinuria and 8-fold higher rate of severe LN flares | Genetically elevated sIL7R highest in the islet cell destruction phase, the target for Tzield |
ABS Identified a Prevalent Genetic SNP That Drives sIL7R Overexpression

Upregulated sIL7R leads to elevated IL7

SNP rs6897932 Exacerbates Autoimmune Disease by Upregulating sIL7R

NIH Demonstrated the Mechanism of Causality:
sIL7R Drives T Cell Expansion and Disease Severity in Animal Model

ABS Demonstrated sIL7R Causality in a Non-Human Primate Study of Multiple Sclerosis

EAE MOUSE CHALLENGE
ABS Confirmed sIL7R Causality in a EAE MOUSE CHALLENGE study

High sIL7R Confers a Significantly Higher Risk of Anti-TNF Therapy Failure in RA

PRODUCT PIPELINE
ABS Portfolio of Therapies and Biomarkers Enables Personalized Immuno-Corrective Therapy for A Genetically Defined Population
ABS mAbs and ASOs reduce sIL7R in the risk population
ABS biomarkers seek to identify responder populations for current or emerging standards of care
sIL7R is an Amplifier of Autoimmune Responses. Elevated sIL7R drives the expansion of T cells, including autoreactive T cells, and amplifies the autoreactive immune responses that drive autoimmunity.
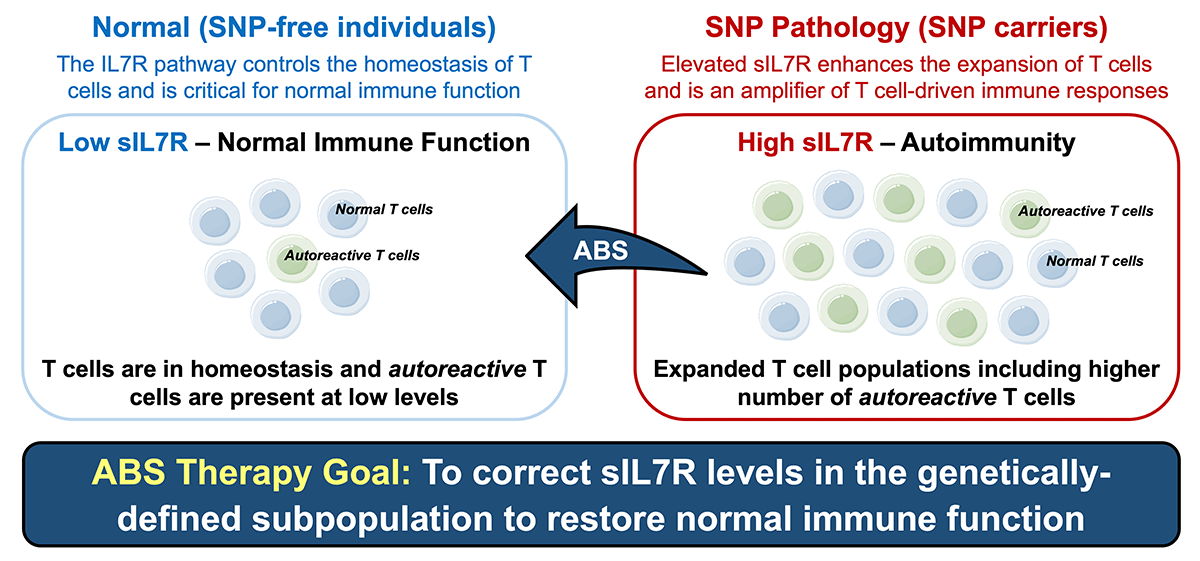
sIL7R is a Central Autoimmune Pathway: ABS is addressing a genetically-defined subset of patients with the SNP and elevated sIL7R, which is associated with greater risk of disease, poor response to therapy and greater disease severity in multiple autoimmune diseases.
Scientific evidence supports the role of sIL7R as a factor in T-cell enhancement and implicates sIL7R as a root cause of disease severity in many autoimmune diseases:
-
Lupus Nephritis
-
SLE
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis
-
Sjogren’s Disease
-
Type 1 Diabetes
-
Ulcerative Colitis
-
Crohn’s Disease
-
Psoriatic Arthritis
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
-
Primary Progressive MS and Relapsing MS
Key Supporting Literature
S. G. Gregory et al., Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nature Genetics 39, 1083-1091 (2007). [PMID: 17660817]
This study uncovered genetic and functional association of the IL7R gene with increased multiple sclerosis (MS) risk, and identified the SNP rs6897932 as the likely causal variant. Mechanistically, the risk allele of this SNP was shown to increase exclusion of exon 6 from IL7R pre-mRNAs, leading to a higher fraction of IL7R RNAs encoding the soluble form of IL7R (sIL7R) and enhanced MS risk.
G. Galarza-Munoz et al., Human Epistatic Interaction Controls IL7R Splicing and Increases Multiple Sclerosis Risk. Cell 169, 72-84 e13 (2017). [PMID: 28340352]
This study showed that the splicing factor DDX39B controls expression of sIL7R and is also associated with increased MS risk. Most importantly, it showed an epistatic interaction between MS risk SNPs in IL7R and DDX39B enhances sIL7R expression and MS risk by 3-fold, thereby underscoring the importance of splicing of IL7R exon 6 and sIL7R expression in multiple sclerosis. This study established rs6897932 as the likely causal SNP explaining the association of IL7R with MS and the resulting up-regulation of sIL7R as the driver of MS these patients.
V. Badot et al., Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts produce a soluble form of the interleukin 7 receptor in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Cell Mol Med 15, 2335-2342 (2011). [PMID: 21129157]
This study showed that sIL7R is elevated in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and the levels of sIL7R correlated with poor response to anti-TNF therapy (infliximab) in DMARD-resistant RA patients. Specifically, 56% of infliximab non-responders exhibited high sIL7R levels, compared to only 15% of
responders. Furthermore, sIL7R levels accurately predicted the response to infliximab therapy: patients with low sIL7R had an 87% probability of responding, while those with high sIL7R had only a 29% probability. This study exemplifies the potential of sIL7R to significantly impact treatment response in RA,
and underscores the potential of sIL7R as a prognostic marker of treatment response, for which ABS possesses proprietary assays.
B. Rovin et al., A secondary analysis of the Belimumab International Study in Lupus Nephritis trial examined effects of belimumab on kidney outcomes and preservation of kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis. Kidney International 101, 403–413 (2022). [PMID: 34560137]
Post hoc analysis of a Phase 3 trial in 448 LN patients comparing belimumab (Benlysta, anti-BLyS IgG1 monoclonal antibody) versus placebo with standard therapy [Belimumab International Study in Lupus Nephritis (BLISS-LN)] showed a variable response of LN patients to belimumab depending on the baseline level of proteinuria. Specifically, this study showed that add-on belimumab improved the primary efficacy renal response (PERR) and complete renal response (CRR) in LN patients with a baseline urinary protein / creatinine ratio (uPCR) < 3 g/g but not in patients with a baseline uPCR 3 3 g/g. Given elevated sIL7R
correlates with greater 24h proteinuria and uPCR in LN patients (Lauwerys 2014; Zhou 2017; See Section IV), it is likely the elevated sIL7R drives this lack of response by high uPCR.
L. Belarif, et al., IL-7 receptor influences anti-TNF responsiveness and T cell gut homing in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest. 29(5): 1910-1925 (2019). [PMID: 30939120].
This study investigated differential gene expression in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients who did not respond to anti-TNF or anti-α4β7-integrin therapy. The authors found that IL7R and an IL7R signaling signature were upregulated in non-responders, suggesting high IL7R activity. Although sIL7R levels were not measured, it is likely that the IL7R signaling signature is driven by elevated sIL7R levels. This study adds further support of the potential impact of sIL7R in driving treatment response in autoimmune diseases.
W. Lundstrom et al., Soluble IL7Ralpha potentiates IL-7 bioactivity and promotes autoimmunity. PNAS 110, E1761-1770 (2013). [PMID: 23610432]
This study further validated the role of the SNP rs6897932 in enhancing sIL7R expression in MS patients and demonstrated direct causality of sIL7R in the development of multiple sclerosis by direct injection of recombinant sIL7R in the mouse EAE model of MS. The authors demonstrated that sIL7R enhances IL7
bioavaliability and potentiates IL7 signaling, leading to enhanced proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and exacerbated EAE. Note: The sIL7R challenge EAE mouse model described here will be the model utilized to establish proof of concept of the top 4 anti-sIL7R mAb leads in the first Seed tranche.
V. Badot et al., Serum soluble interleukin 7 receptor is strongly associated with lupus nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 72, 453-456 (2013). [PMID: 23264357]
This study showed that sIL7R is elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and is strongly associated with nephritis in these patients. Specifically, sIL7R serum levels were elevated in SLE patients over controls and were the highest in LN patients. In both SLE and LN patients the levels of sIL7R strongly
correlated with disease activity, as determined by SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) scores. Interestingly, the levels of sIL7R in LN patients decreased following immunosuppressive therapy and significantly correlated with a drop in SLEDAI scores. These results strongly support a role of sIL7R in the development of LN.
20. B. R. Lauwerys et al., sIL7R concentrations in the serum reflect disease activity in the lupus kidney. Lupus Sci Med 1, e000036 (2014). [PMID: 25396066]
This study showed that sIL7R levels correlate with disease activity in lupus nephritis (LN) patients, including the urinary protein to creatinine ratio and BILAG A. Importantly, this study showed that LN patients with high levels of sIL7R exceeding those seeing in SLE patients (renal cutoff level) had an 8-fold
greater risk to have severe renal disease (BILAG A flare) within 3 months of surpassing the renal cutoff level (48% in LN patients above sIL7R renal cutoff versus 6% in patients below renal cutoff). Besides the correlation with severe renal flare, the authors also showed a correlation of sIL7R with markers of poor kidney function such as the urinary protein to creatinine ratio. These results strongly support a role of sIL7R in driving the severity of renal disease in LN patients.


Our Approach: Immuno-Corrective Therapy to Restore Normal Immune Function
Immuno-Suppressive vs Immuno-Corrective Treatments:
Immuno-Suppressive – Current autoimmune disease treatments, including standard of care and pipeline drugs, target components of the immune system essential for normal immune function. While this approach is effective in preventing autoimmune responses, it also hinders the capacity of the immune system to provide protection against pathogens and malignant transformation, leading to adverse effects associated with immunosuppression.
Immuno-Corrective – The ideal autoimmune disease treatment would target the root cause of the autoimmune reaction while sparing protective immunity to restore normal immune function – a corrective treatment. In line with a precision approach to autoimmunity treatment, ABS corrects a fundamental pathway that causes autoimmune disease to prevent autoimmune attacks without causing immunosuppression – in other words, to restore immune homeostasis.
ABS Selectively Targets sIL7R for Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases by Restoring Immune Homeostasis Without Causing Immunosuppression.
Akin precision treatments in oncology, ABS’ anti-sIL7R monoclonal antibodies correct the root cause of the autoimmune pathology in the genetically-defined subpopulation of autoimmune disease patients.
ABS developed the first monoclonal antibodies that specifically inhibit sIL7R while sparing the canonical membrane-bound IL7R.

By discriminating between the soluble (sIL7R) and membrane-bound (mIL7R) isoforms of IL7R, ABS’ anti-sIL7R monoclonal antibodies selectively drive the therapeutic effect of sIL7R inhibition without inducing the immunosuppressive side effects of mIL7R inhibition.
